光子学报
2022, 51(11): 1114002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 Institute for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
3 School of Physics and Electronic Science, Hunan University of Science and Technology, Xiangtan 411201, China
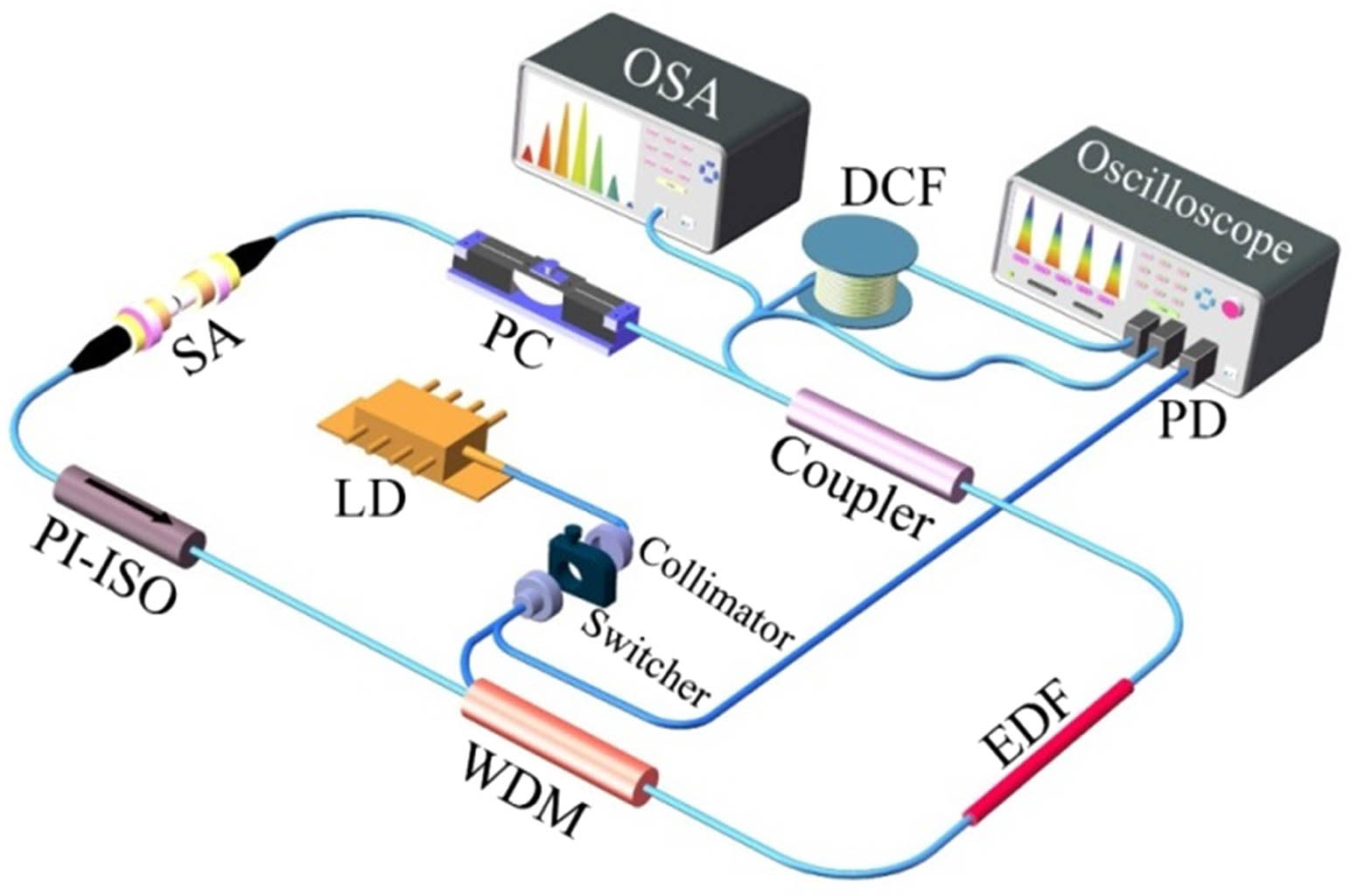
The dispersive Fourier transform (DFT) technique opens a fascinating pathway to explore ultrafast non-repetitive events and has been employed to study the build-up process of mode-locked lasers. However, the shutting process for the mode-locked fiber laser seems to be beyond the scope of researchers, and the starting dynamics under near-zero dispersion remains unclear. Here, the complete evolution dynamics (from birth to extinction) of the conventional soliton (CS), stretched pulse (SP), and dissipative soliton (DS) are investigated by using the DFT technique. CS, SP, and DS fiber lasers mode locked by single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) are implemented via engineering the intracavity dispersion map. The relaxation oscillation can always be observed before the formation of stable pulse operation due to the inherent advantage of SWNT, but it exhibits distinct evolution dynamics in the starting and shutting processes. The shutting processes are dependent on the dispersion condition and turn-off time, which is against common sense. Some critical phenomena are also observed, including transient complex spectrum broadening and frequency-shift interaction of SPs and picosecond pulses. These results will further deepen understanding of the mode-locked fiber laser from a real-time point of view and are helpful for laser design and applications.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(4): 04000423

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhejiang University, College of Optical Science and Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Hangzhou, China
2 Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Institute for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research, Nanjing, China
3 Hunan University of Science and Technology, School of Physics and Electronic Science, Xiangtan, China
Real-time spectroscopy based on an emerging time-stretch technique can map the spectral information of optical waves into the time domain, opening several fascinating explorations of nonlinear dynamics in mode-locked lasers. However, the self-starting process of mode-locked lasers is quite sensitive to environmental perturbation, which causes the transient behaviors of lasers to deviate from the true buildup process of solitons. We optimize the laser system to improve its stability, which suppresses the Q-switched lasing induced by environmental perturbation. We, therefore, demonstrate the first observation of the entire buildup process of solitons in a mode-locked laser, revealing two possible pathways to generate the temporal solitons. One pathway includes the dynamics of raised relaxation oscillation, quasimode-locking stage, spectral beating behavior, and finally the stable single-soliton mode-locking. The other pathway contains, however, an extra transient bound-state stage before the final single-pulse mode-locking operation. Moreover, we propose a theoretical model to predict the buildup time of solitons, which agrees well with the experimental results. Our findings can bring real-time insights into ultrafast fiber laser design and optimization, as well as promote the application of fiber laser.
fiber laser mode-locking self-starting process relaxation oscillation real-time spectroscopy Advanced Photonics
2019, 1(1): 016003





